-
Publish Your Research/Review Articles in our High Quality Journal for just USD $99*+Taxes( *T&C Apply)
Offer Ends On
Hsiao-Dao Chang*, Song-Jang Chen, Chih-Kuei Chen, Chi-Ming Yang and Chao-Ying Chen
Corresponding Author: Hsiao-Dao Chang, Ph.D. M.S, Agriculture Chemistry, Bio-Chemistry, Safety, Health and Environmental Engineering, Ming-Chi University of Technology, Taiwan
Received: February 10, 2021 ; Revised: March 28, 2021 ; Accepted: March 31, 2021
Citation: Chang HD, Chen SJ, Chen CK, Yang CM & Chen CY. (2021) A Assessment of Soluble Humus Hydrolysate from Flammulina Velutipes Waste Post Molecular Sieving as Nutrient Stabilizer. Adv Biotechnol Biopro Res, 1(1): 1-13.
Copyrights: ©2021 Chang HD, Chen SJ, Chen CK, Yang CM & Chen CY. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Views & Citations
Likes & Shares
The mineralization of biological waste usually needs years of hydrolytic time for dealing degradation and reformation into humus matter for stabilization of microbial community in soil and regulation of nutrient release. In this study, recovery of small, soluble humus hydrolysate (SHH) from Flammulina compost via chemical, acid catalysis had achieved in a new way. The shredded the mushroom fermented waste was further shredded, Acid’s catalysis hydrolysis (sulfuric acid / catalyst) under steam heating with only 46 min. A harvest pool of 5-45 kDa molecular sieving harvested as SHH, these 30 % of active melanoid collected shown effective for soil conditioning and in providing higher nutrient needed for sunflower nourishing to full seedling maturation stage. It showed more promising as ever compared to compost fertilizer result with only half of its growth. FTIR spectrum indicated multi-functional peak appeared when bonding broken. While reduce ring size, with unique adsorption band - 370 ~ 490 nm exerted important for evaluation of existence and quality for melanoid product. Also, SHH could intimately with EM when combined used in spreading after mid cultivation stage. Among consortia combined in the fertigation, photosynthetic as the best for fertility effect resulted, from seedling to ripe fruiting. These finding indicate the chemical hydrolytic way might perceived to be an important route for fasten productivity for production an effective organic matter for soil restoration, environmental restoration for sustainability.
Keywords: Acid catalytic hydrolysate, Soluble humus hydrolysate, Effective micro-organisms, Photosynthetic microbes, Plant growth promotion
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
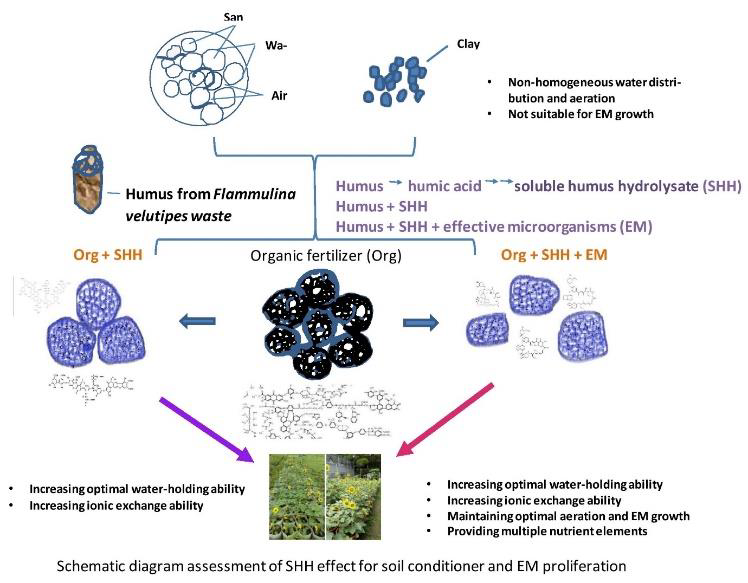
STATEMENT OF NOVELITY
INTRODUCTION
The quantities of recyclable biomass in US counts for over 40 % of the total organic waste and almost exceeds 4 times of municipal solid waste dumped into landfills. These resources processed and converted into soil conditioner via humus for agriculture or developing new cultivable area. It was prospected the cultivation of energy crop would expand into equally enlarged agriculture crop for the coming shortage of energy or climate change issue. The changing of cropped land for example unexpected, even the coldest region became greenish while warming. As European Union has estimated that farming area will reach 200 million hectares (mh) within 50 years, also extra enlarged its plant area for energy crops, reached 100~200 mh expanded within the peripheral and developing area for non-food purpose. These policies direct the needs for enlarging green energy production and reduce CO2 emission were urgent for restoration of ecological change as well as for food production. Thus, the changing of vegetate technology would demand high quality of culture media, fertigation method in production by process and technologies. The processing of mushroom cultivation bio wastes presently indicated as an example for rapid stabilization and recycle use. The successful practice would demonstrate the potential implementation for the future. Based on the fact, about 1.7 X 103 million tons (mt) of biomass was presently unused yet and dumped. only 140 mt recycled through agriculture farming [1]. It indicated that the changing of plantation pattern would be challenged by require of 500 mt. yr. annually for new product in the near future. The necessity of efficient recycling of lignocellulose into highly efficient of soil conditioner well be the economical need which challenged the conventional natural weathering process. The effective melanoid process and biotechnology could help the fastened-up stillage application for ecological need at demand by proper formulation designed while lowered plant pest and disease risk.
Beside market requirement, SHH might provide 3 benefits aspect. First, a tool to lower the coming pressure from food demand for raise up over 75 million of people. SHH could be the fastest route for fasten organic waste recycle to agriculture production. Thus, reduce sustainable ecological problem. It connected equilibrium to soil microbes, the cycling of N-P and stabilization of organic matter (OM) for recycling. These were crucial quality and benefit to all life form to sustain the
soil ecological cycle. Roughly estimated, over 2.65 X 105 mts of humus derived from organic waste potentially needed by physical-chemical mediated reaction. The present study indicated the development seem possible and effective. The compatibility with com-bine effective microorganism was crucial to the extension practice of farm tillage.
Second, speed up with the delivering of nutrient with precisely measurable base were possible because SHH engineered to be nano-molecule had better con-trolled nutrient level by adsorbing and regulate by functional group in the hydrolyzed molecule. These properties led to totally changed and uniformly growth appeared even in field tillage. Contrary to conventional practice, usually need constantly survey under territory with particular environmental controlled event, e.g., flooding scenarios [2], proper watering example for dry regions in China [3], microbial respiration rate based were successful correlated despite complicated factors for evaluating cultivable species by specific calories - heat content of soil assessed [4]. Also, advanced aquaponics in plant factory study, suggested SHH could be integrated as precision irrigation and fertigation by in liquid phase.
Mushroom fermentation, composting of organic waste via humus, which im-prove soil aeration, C/N ratio, colonization of effective microorganism, etc. [5-7]. Humus hydrolysate had the properties for micros taxis and regulation in nutrient fertigation [8-10]. In this report, A catalytic way to generate soluble pool of melanoid for soil conditioning effect were found excel effective, further compatible to effective microorganism for enhancing nutrient element NPK were indicated by field plant growth.
Such that Steamed heat catalytic process conducted presently had proved its screened pooled by molecular sieve could identified by spectrophotometry, chromatography to get molecular size profiles, combined fertigation into organic fertilizer was succeeded also by amended with photosynthetic consortium via liquefied processed.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Agricultural Waste, Humus and Chemicals
Flammulina solid waste obtained from one cultivation plant at Dong Shi, near Taichung City, Taiwan. They were first air dried and crushed by branch shred-der, also soybean mill waste was taken from soap store in Yung Ho City, New Taipei City as liquid fertilizer C, N source. Hydrolyzing catalytic minerals and trace chemicals of purity grade obtained from Merck and Sigma (USA), purchased and utilize in microbial acclimation medium, sulfuric acid purchased from Tai Hua chemical engineering Corp., Taisan, New Taipei City.
Composting, Acid Catalytic Hydrolysate Treatment for Harvesting SHH
Composting of fermented Flammulina waste (FW): The woody fermented waste from Flammulina was blended first (Electric 1 hp Chipper Shredder, USA) and mixed with waste soybean mill with a 60: 40 ratio (w/w), equilibrated to 60% water content, then bottom aerated with ratio of 0.2 L air / L solid waste. Composting continues with biological oxidation for a minimum of 2 weeks [11], then proceed-ed the hydrolyzing procedure (FW COM).
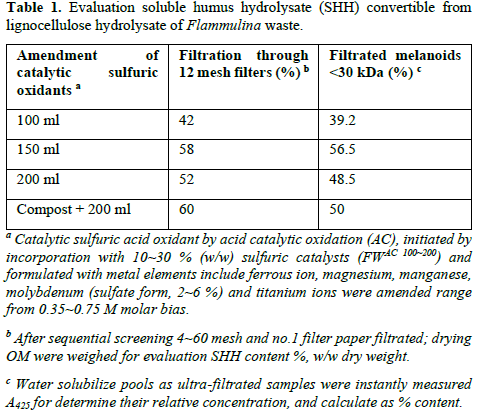
Acid catalytic hydrolysis: The hydrolyze by acid catalytic oxidation (AC) was initiated by incorporation with 10~30% (w/w) sulfuric catalysts (FWAC 100~200) and formulated with metal elements include ferrous iron, magnesium, manganese, molybdenum (sulfate form, 2~6 %) [12,13], and titanium ions were amended range from 3.75~7.5 (v/w) which calculated to be 0.35~0.75 M in molar basis [27-29]. After the mineral elements were amended homogeneously into com-post, then sulfuric acid was added to initiate the reaction in the 15 L polypropylene bottle for 48 min in steam, autoclaving at 121℃, 1.2 kg/cm3 condition. After hydrolyzing, cellulosic waste were transferred and processed by rinsing 10 volume of DI water for releasing SHH portion [14,15]. Eluent involved blending with wood peddle then passing it through 4,12,60 mesh for screen out insoluble solids. The har-vested eluent dehydrated to dryness before weighing for evaluate harvest ratio. After serial molecular sieving to collect extract soluble humus hydrolysate (SHH), collected pool were desiccated and proportionated dissolved with solvent involve ace-tone, acetonitrile, and double de-ionized water, with ratio of 30:40:30 (v/v). The sample was filtered through No. 1 paper (Advantech) and analyzed by a solid phase - C18 column equipped ELSD-HPLC [16] (ELSD 1000, polymer lab, column heating ambient ~ 60℃) for analysis [17].
Evaluation of Harvest Soluble Humus Hydrolysate (SHH) from Hydrolyzed Flammulina Waste
Evaluation SHH convertible from lignocellulosic hydrolysate, after drying (105℃) of sieving out portion, the SHH content was calculated evaluated: [A (Coarse sieving portion) - B (molecular sieving)] / A X 100, in dry weight basis for each treatment. The organic weighted based on standard methods (ASTM D2016-65, 1102-56). With further evaluate the water solubilize pools as ultra-filtrated samples were instantly measured in 425 nm for determined their relative concentration based on absorptive properties. Relative content was evaluated by absorbance ratio obtained. In exchange of ionic strength, coarse organic matter was dialyzed against 10 mM, pH 7.2 phosphate buffers. Dialyzed (FuBio CF 7931,40) through 2.4 nm pore, exchangeable matter lyophilized and exchanged for chromatographic HPLC, then analyze by spectrophotometry.
Characterization of SHH by Spectrophotometric Analysis
After steam & acid catalyzed hydrolysis, sample was screening. The eluent from molecular sieving pools with different molecular size analyze by measurement on UV/VIS spectrophotometer. Wavelength scan range from 190~790 nm, absorbance at 280, 425, and 490 nm were exquisite for
estimating their SHH relative concentration. A425 was experimentally indicative for every sample collected. They were prepared for further FTIR analysis. Samples was manipulated in a ratio of 4 mg/kg prepared. Desiccated and homogeneously pressed with KBR, the salt pellet was scanned in infrared spectrum - 400~4000 cm-1 by infrared spectrophotometer (Perkin Elmer, Spectrum 100N FT-NIR) [18].
Evaluate SHH Content by Molecular Sieving Column
The SHH extracted and processed with neutralization and eventual molecular sieving. The screen pool was conducted by passing molecular sieving tube (LEF Science, model: MAPO1-TFF, PES, 20 m2), which. The molecular weight was ultrafine sieved from 30~4.5 kDa, the elute efficiency was speeded by their hollow fiber structure.
Acclimation Effective Microorganism by Compost - SHH, Reducing Medium
Acclimation of the effective consortium using kitchen compost and combined reducing medium, in which active microbes were proliferated through nutrient and solubilized SHH. Solution of kitchen compost was mixing in equal volume of reducing medium. The modified composition contained (g l-1): (NH4)2SO4 (1.0), FeSO4∙7H2O (0.005), K2HPO4 (1.0), CaSO4 (0.5), black sugarcane sugar (1.0), amino acid mixture (Primex Marine Peptone) (0.5) and ½ of a tablet of vitamin B per liter; trace element include (g l-1): HBO3 (0.005), MgSO4 (1.0), KI (0.005), (NH4)2SO4 (1.0), FeSO4∙7H2O (0.01), Na2SO4 (0.3), K2HPO4 (0.3), CaSO4 (0.5), ZnSO4 (0.001), MoSO4 (0.001) [19]. The medium was fed with equal volume and controlled with an HRT of 10 days to acclimate for 6 months for enriching microbes in 10 L PVA sponged fixed film column. In study the microorganisms existed, sludge was serial diluted for facultative culture with the same acclimated medium. Microbe community was single colony isolated and sub-cultured to pure and identification through 16S rRNA genetic method. The selected Bacillus spp. were culture and re-inoculated into 30 % (w/v) granular organic fertilizer (Org) ratio in a 15 L PP sealed bottle; Different OM from kitchen waste compost, soybean mill and granular organic fertilizer were parallel proceeded. After fermentation gas produce in mass formation, then inoculate 1 L (6 %, v/v) bacterial concentration was continuous proceeded monthly. Under deem light, photosynthetic consortium (PSC) produced in superficial peripheral region, weekly shaking was adequate for enhance gasification and dominate PSC proliferation for use.
Evaluation of Nutrition Effect by Planting and Fertigation Sunflowers
In test of fertility by planting sunflower based on its fast growth in subtropical region for adapted to the humid and hot climate. The efficient of nutrition acquisition was due to their herbaceous variety. Seedling’s stage was prepared from initial breeding bed (20 holes/rack), and 3 weeks later, transplanting their 10~15 cm seed-ling height was adopted. at least 80 plastic pots with 240 seedlings were transfer for duplicate analysis. Plantation use YanMing soil as basal media, implement approx. 3% (w/w) organic matter for soil conditioning, and also with 4.5% (w/w) organic fertilizer (from Formosa Plastic Corp., No. 1, TN/TP/K2O = 5:4:4) for providing NPK nutrient source [20]. The amount of soil in vase was putting 40 L media for planting in the same condition. To continue the breeding process, SHH solution with A425 0.35~0.4 was applied to combined with EM broth (600 dilution) and sprayed every 10 days, 1 L for each vase [21,22]. Before full blooming period, 50~100 ml of EM broth was irrigated around the root for boost of maturation to complete seed production.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
For long time, researchers interested in trying distinguished among oxidation mediated brownie compound formation. Particular of the mechanism involve molecular reducing or intercalating property like surfactant. The art of bond breakage and rearranging of organic matter by heat, steam - hydrolysis in extreme pH or enzyme mediated reaction with harvesting compound broadly reported in many systems [23-25]. But rarely had study involve systematically report about the product of Maillard or cabamelization [26], lignocellulose hydrolysate, composting, etc., for their structure complexity and product hard to separation and analysis. However, through modified acid mediated catalytic hydrolysis by amend catalyst ion e.g., Mn++, Mg++, Mo++, Ti+++, catalytic breakage, rearranging, nitrogenous biomass via Flammulina cultivation waste was hydrolyzed in a mild energy steam heat / acidic condition, solubilized humus hydrolysate (SHH) was studied by hydrophilic ex-traction, a Green way of production soluble hydrolysate was establishing for ecological engineering application.
Categorize SHH Pool Through Molecular Sieving
In attempting to separate SHH pool and improve harvest ratio by molecular sieving process. Before treatment by acid catalysts hydrolyses, parallel harvest of SHH by expending waste streams such as mushroom fermentative bodies, its com-posted biomass, and initial lignocellulosic matters. Evaluation analysis were by instrument analyze with initial separate of molecular pool.
In the separation trials, SHH pool from hydrolyzed biomass, after sequential molecular column from 30~4.5 kDa. Under strong dose of metal ion effected for biomass hydrolysis, currently we found SHH releasing through intermittent mixing for reactant transfer. After filtration through 12 meshes and no.1 filter papers, the filtrate of SHH total sizeable portion (Figure 1A). When providing rotary mix pretreated and screen 12-mesh sieving, No. 1 filter paper It was shown the recovery of SHH ( FW AC-7.5 -52% > FWAC-3.75 -42.5 %, while FW COMAC-7.5 treated were still the highest - 60% (Table 1).
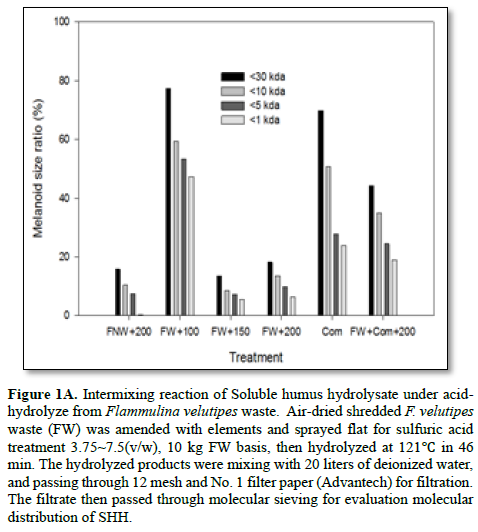
It was further illustrated the SHH releasing by low shear stress through rotary mixing and macro pore screening was effective releasing and avoid possible coagulation, precipitation on the filter paper, such that molecule - Flammulina culture media were the least collected. These results supported that pretreated with biologically fermented, either compost or mushroom fermented could loosen the humus structure and ruptured by acid catalyzed hydrolytic reaction. These biological wastes might be solubilized by way of medium steaming temperature. The SHH compound could become as distinct pool from 1 ~ 30 kDa. The optimal acid dosage for FWAC 5 series (Table 2) observed appeared better ration between reactant to catalyst (Figure 1B).
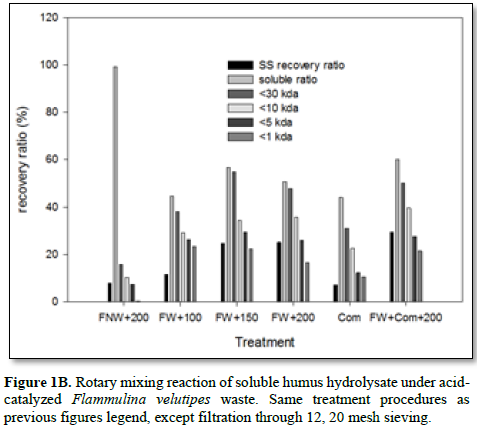
1.png)
1.png)
Investigation of SHH Product Distribution by Chromatography
The analytic technique for humic acid using RP column - HPLC couple with ELSD detector was succeeded for visual its distribution. Mobile phase was run by conducting less polar attraction for hydrophilic SHH, with acetone, acetonitrile pulling, result fast eluted by packing 5~10 μm bead of C8 column. The detection by scattering light detector is sensitive for visualization colored compound, Fast eluted profiles could be separated into 3 collection groups with RT 3~4, 6~7.5, and 7~9 min fractionated. The significance of these results revealed FWAC-3.75, FWAC-7.5 hydrolyzed pool, with 5 kDa molecule pool had similar RT (Figure 2A). While amino acid hydrolysate processed through steamed pressure & temperature, contain amino acid derivatives, which appeared as lowered concentration and lower SHH content harvested (Figure 2B). As for soybean cakes, hydrolyzed by PSB sortie had a slower RT for SHH pool and possible larger molecular size pooled. In com-pared, difference between FWAC-3.75, FWAC-7.5 treated, the former showed smaller molecular size, while FWAC-7.5 had larger molecules instead. While the product of amino acid from hydrolyzed protein also possessed medium sized SHH beside clustered peak of amino acid (Figure 2C). Last, smaller size and low content appeared in the hydrolysates of soybean bran waste, < 5 kDa hydrolyzed molecule by acclimated consortium of Pseudo-Rhodococcus spp., resulted a smaller fast-moving peak, indicate limited soluble SHH from insufficient hydrolysis and transformation (Figure 2D).
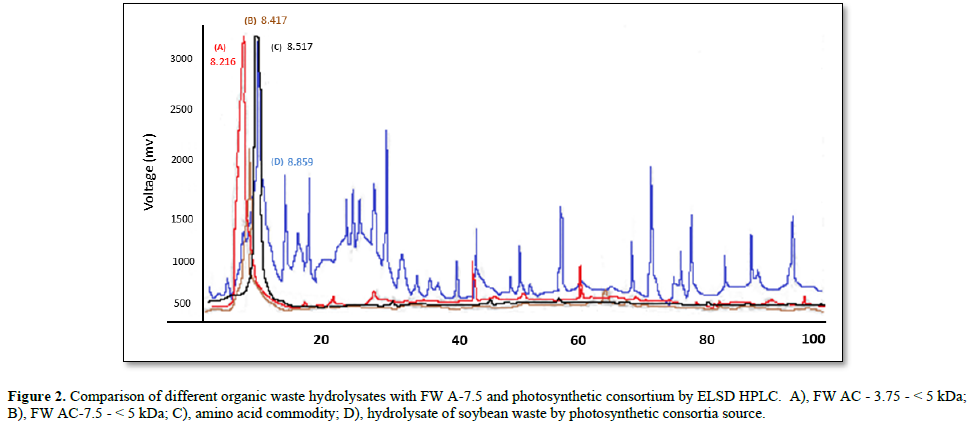
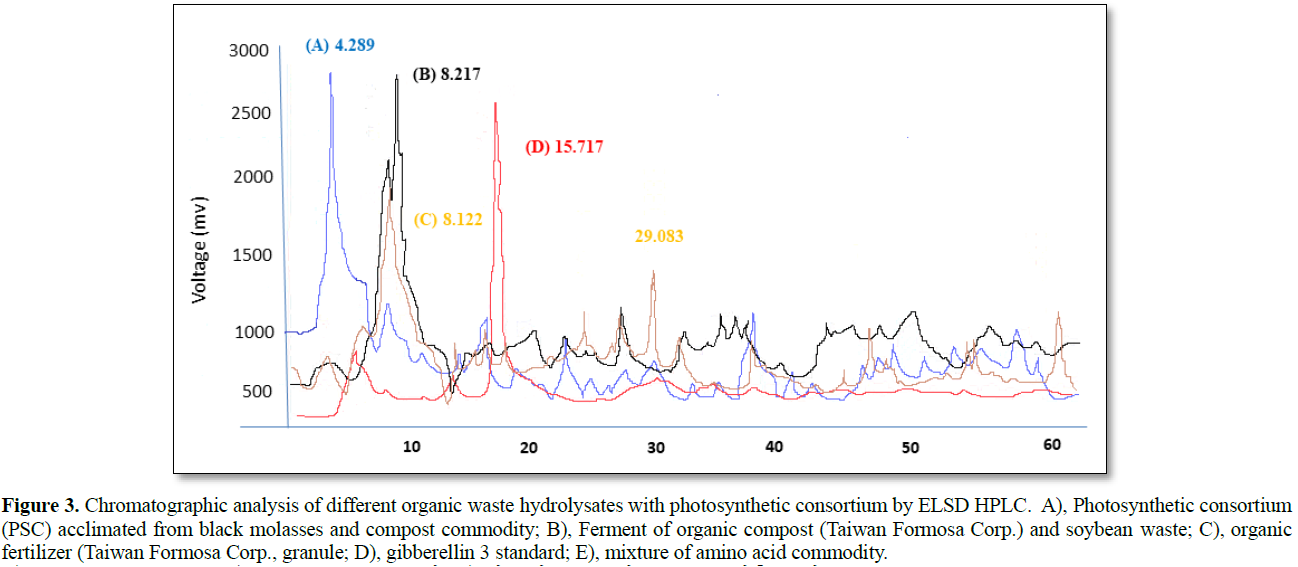
In further observation the biological effect on SHH production by different acclimated PSB consortia, results shown that biological SHH from added OM as Figure 3A, which combined molasses and soybean brans resulted medium size of SHH peak with its RT shifting forward, indicate abundant of hydrolysate ingredient produced. Biological oxidation by PSB consortia exhibited multiple sharp peaks with slow RT, meant produced varied metabolites by bio-hydrolyzing activity. It was also through co-fermented with SHH and granular organic fertilizer (kitchen compost, Formosa plastic. Ltd., no.1 fertilizer). During SHH releasing, co-fermented with granular fertilizer anaerobically for half a year still intact for no discernible soluble product (Figure 3C), The extent of hydrolyzing product seems not changing with progress of incubation, also the molecular size distribution remains stable (Figure 3B). Analytical profile as GA3, the RT peak appeared at RT 15.71. Much slower compared to the SHH in amino acid commodity (Figures 3D & 3E). In conclude of reverse phase separation, the eluent of high hydrophilic SHH through polar mobile phase result fast movement for large molecular [20]. It supports that SHH is suitable for high oxidizing mechanism pretreated and released.
Determine the Surface Property of SHH Hydrolysates by Spectrophotometry
Since Fulvic acid, a kind of small humic acid has its amphipathic property, with its acid soluble while folding and precipitation at neutral pH, best natural soil conditioner reported [30]. They were part of the humus in compost product [31]. Presently, we investigate SHH properties and molecule for usage as conditioner and EM co-fertigation for application [32].
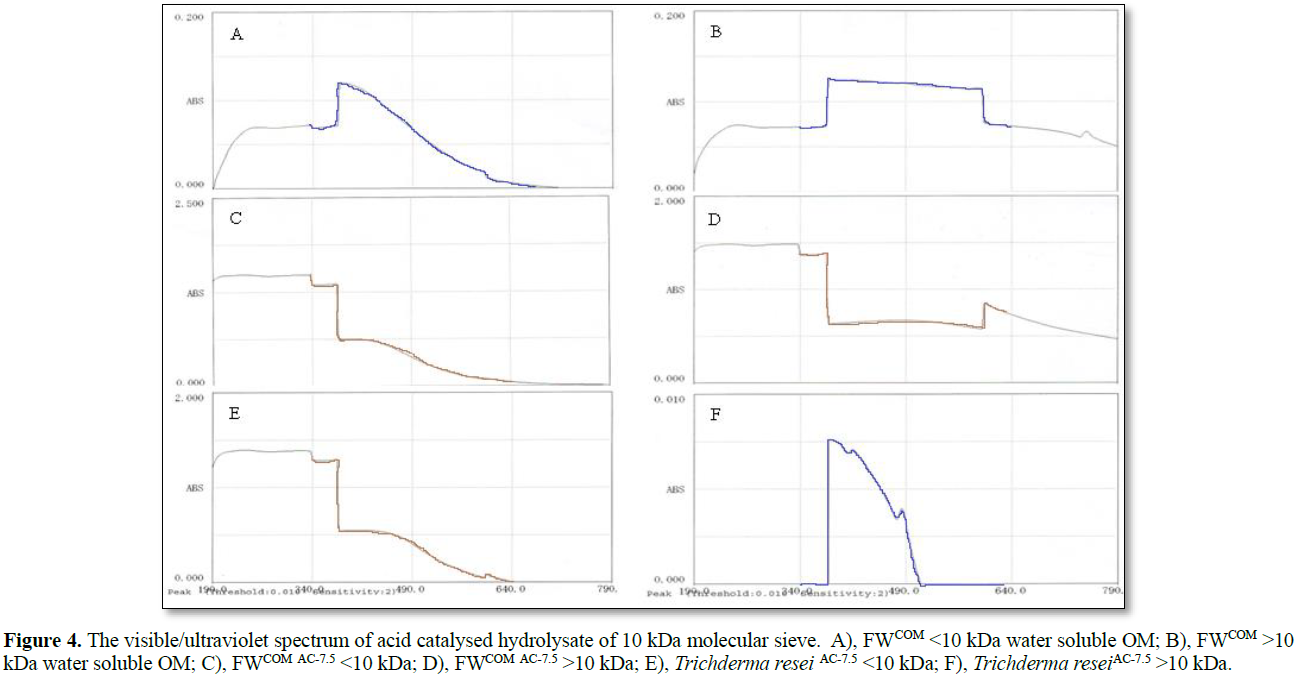
Present advanced survey the surface property of SHH, scanned UV/VIS data for all sample elucidate similar structure and functional group existed. As inspect of UV/VIS spectrum have smooth adsorption within 360 ~ 490 nm chromogenic band obtained. This indicated the grafting group linkage to the aromatic ring, unsaturated heterocyclic nitrogen, conjugated bond was indicative for quantitation comparison. In addition, in SHH were spectrum identical for molecule < 10 kDa as well (Figures 4A & 4B), and highest absorbance appeared in FWCOM and SHH pools for molecule > 10 kDa as well. Also, biomass steam-catalysis product of fungi as Trichoderma resei, absorbance spectra with 10 kDa molecule exist (Figure 4E). Even the content evaluated only 10 % of FW origin. That means low density of similar compound produced in catalytic hydrolysate of Fungi biomass. It meant this emerging pool had already existed in compost and identifiable when separation proceeded. It also perceivable that dissolved product after molecular sieving also observable, even in other natural organic matter through hydrolyzing procedure and pooled SHH molecule < 10 kDa (Figures 4C & 4D). These data support the idea that this reaction have profound tolerant and driven out their product across various kind of chromogenic biological specimen. The quantification or evaluation of SHH content could calculate based on A425~440 nm measurement. The combining of absorbance and chromatography property might help establish interrelated bonding or intercalating into the vicinity in respect to ex-pending our knowledge about SHH property.
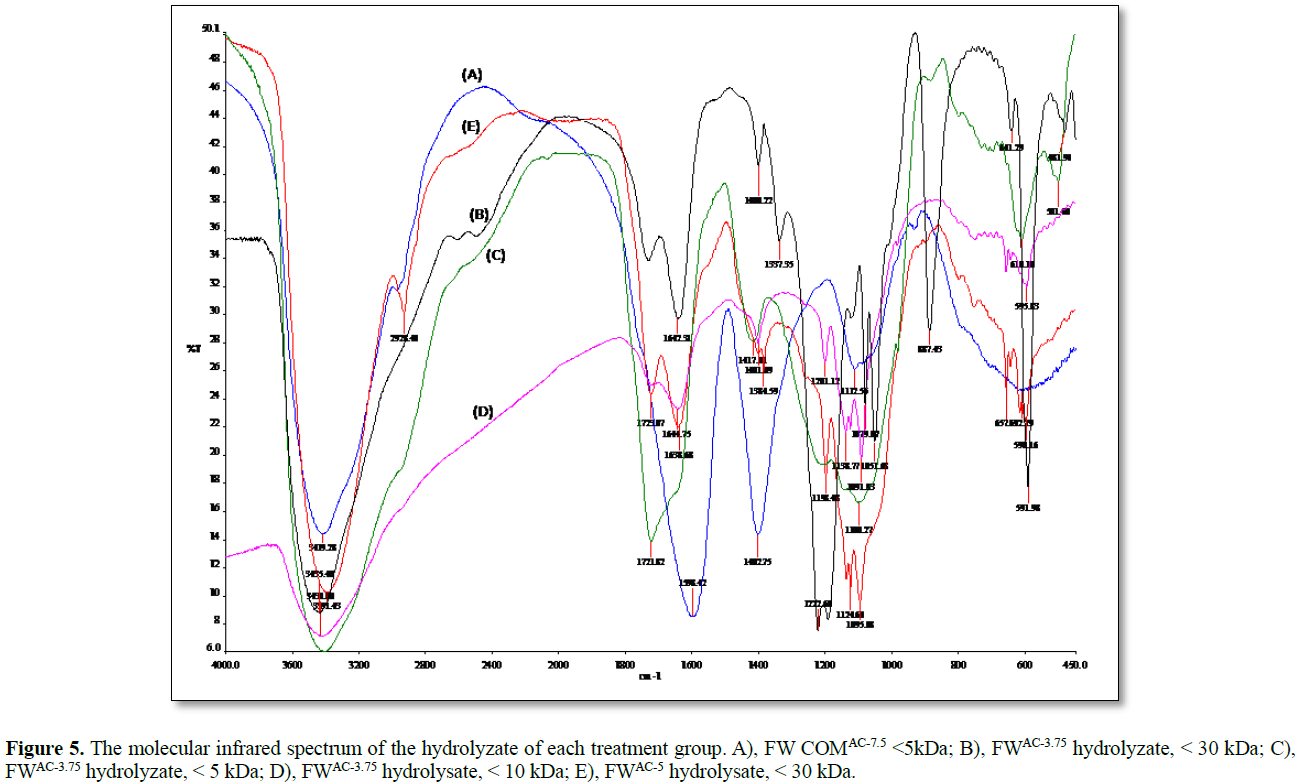
Furthermore, Infrared spectrum support the hydrolysis had changed the sur-face structure of SHH. It was found that original compost leachate sample with 5 kDa sieving, exerted broad spectra with no sharp peak, obvious hydrogen bonding or aliphatic chain appeared at 1110-1115 cm-1, indicate inert surface property which demonstrate more about original surface status than UV/VIS spectrum indicated (Figure 5A). Comparison between FW acid hydrolysate, with acid amended 3.75 %, 5 % treated, harvest < 30 kDa pool, even low acid FW AC-3.75, showed 11 sharp identifiable peaks shown in scanned IR spectrum (Figure 5B). These difference from com-post by protruding functional group included stronger 3400 cm-1, pertaining hydroxyl and originated carboxylic, amine group possible involved. Band at 1600-1700 cm-1, contribute conjugated double bonding originated from phenyl aromatics, carbonyl, and carboxylic connecting aromatic structures. These results protrude the producing of small aromatic molecule from macro humus into humic acid instead. In addition of branched peak appeared at 1400 cm-1, which respond from a carboxylic root, formation important functional group for binding cations, e.g., Ammonium, Potassium ion. Other pools at 1100 cm-1 for grafting methyl group, spirited peaks by methylene vibration with medium strength. These were the key spectrum pertaining aliphatic structures, with similar vibrational energy (Figures 5C & 5D). These spectra paralleled aligned, suggest SHH molecule contain surface’s active groups, as humic acid literately concerned.
With 5 % acid catalyzed SHH, (Figure 5E). These results supported the general appearance of reduce its molecular size. These spectrophotometric data linked these functional properties after bond hydrolyzing, grafting and rearranging into electric or polar attractions matrix. Co-fermentation of SHH and EM were further integrated into the agricultural and environmental remediation applications [33,34].
Fertigation EM Consortia with SHH for Remediation Sunflowers
As generally accepted Fulvic acid exerted strong soil conditioning effect and microbial co fermentation for nutrient regulation [35], it was also empirically use molasses for these purposes. Thus, focuses to construct activate ways for thriving effective microbes for donation phosphate and promoting agent. In present trials, kitchen compost and organic fertilizer ferment, amending 0.5 g/L molasses and basal element through providing years of acclimated incubation. The ripening process shown the ferment maintained the ORP within -20 ~ -80 mv pertaining to a microaerophilic condition, which enable to plate out 106-108 CFU thriving with activity in functioning of element nutrient release and grown crop. Even ten pure isolates were cultured and send 16S rRNAs sequence blast identified by NCBI data. with >99.5 ~ 100% identical. Table 2 showed species most belong to Bacillus groups, which closed to phytopathology antagonistic microbes. These revealed that humic acid with a medium of 1200-1500 mg/L COD strength, successful acclimated anaerobic growth of Bacillus spp. As hydrolysis proceeded, it was shown granular kitchen organic fertilizer (Forma plastic Ltd.) was the origin of SHH produced. As expected, amendment of sugarcane black liquors, facilitated to have soluble pool, but donate low contribution of SHH, but provide carbon source for growth and drive metabolic activity for acclimate EM [36]. In attempting to collect suitable liquid fertilizer through lengthening & acclimation duration, PSB consortia formed naturally and treated as stabilizing for the fertilizer through properly sunlight in the agriculture house. The co-fermentation culture of these EM consortia could proliferate and balanced growth after the initial inoculation.
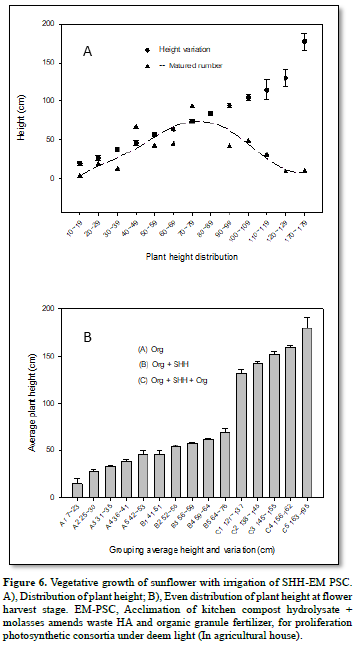
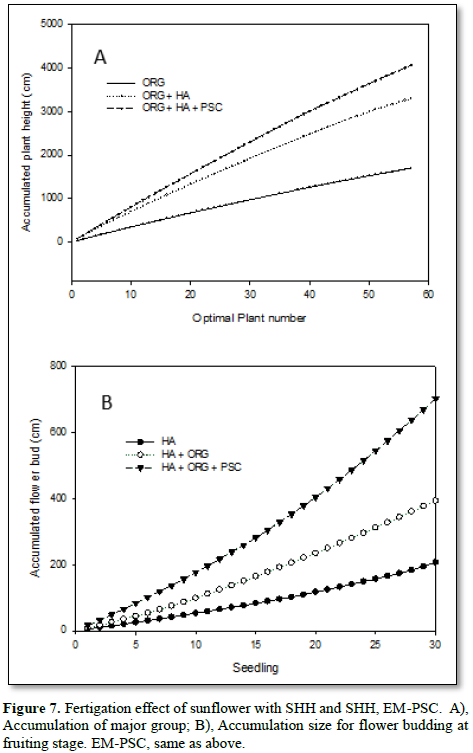
Most commercial products of liquid fertilizer, as PS was designate for flowering & fruiting purpose [37], while EM Bacillus was better for antagonistic of pest and disease in growth stage [38]. In this experiment, we found EM Bacillus with PSC provide bioavailable phosphate beside nitrogen nutrient too. Either organic fertilizer or SHH, provide less fertility as expected (Figures 6A & 6B). These results coincide SHH have grafted polar oxygen or hydroxyl groups related to effect on soil conditioning property. The nano sized molecular facilitated in penetrating through inter-acted biological or mineral agent and responded in growth effect. Variant fertility responded & related to the nature of organic matter, or hydrolyzed product beside EM metabolite, with part of antagonistic microbe with metabolite active agent too. SHH hydrolysate might be the major effect that trigger the equilibrium state beside soil condition by proliferating in growth when integrated in irrigation. The effect for faster nutrient delivery through irrigation contact is prospective, As seen liquid fertigation in this experiment have excellent proliferation for growth and enhance fruiting. These results demonstrated that humic SHH could combine EM for a balanced growth with high fertility for most crop remediation required (Figures 7A & 7B).
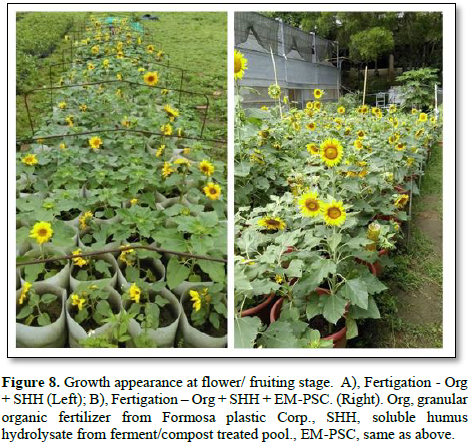
Field observation of lattice breeding of sunflowers successfully discriminate effect over times of experimental compared. Organic fertilizer showed slow release and improved on supplement of SHH, which means its proliferation might directly from profound soil conditioning effect. In addition, boosted effect exerted when combine irrigated with Bacillus-PSC, which believed that active component proliferate growth, their compatible with plant and rhizome community direct eventually reach a PGPR state and direct success cultivation. In conclude, the boost value of liquid fertigation of SHH with EM proved most reliable not only over 50 % more height and fruit obtained of sunflower growth, it generates a planting technology both in waste recovery and reuse for sustainable development, also possible for environmental engineering use in bio remediation implementation (Figure 8).
Combine Fertilizations SHH and EM for Harvesting Sunflowers
As fulvic acid was generally accepted for an excellent soil conditioner effect and microbial co-fermentation ingredient for nutrient regulation [35]. Thus, presently we tested molasses and kitchen waste compost for ferment purposes and construct activate ways for thriving effective microbes for donation phosphate and plant promoting agent. It was further finding that kitchen compost, organic fertilizer ferment, with amending 0.5 g/L molasses and basal element through half a year of acclimated incubation. After ripening for use and showed the ferment ORP maintained with-in -20 ~ -80 mv pertaining to a microaerophilic condition. The ferment enabled to plate out 106-108 bacterial CFU thriving in the ferment. Over ten isolates were pure isolated and send 16S rRNAs sequence blast for identification by NCBI data base. with near 100% identical in base sequence, showed most belong to Bacillus species (Table 2), also closed to phytopathology antagonistic microbes. These revealed that humic acid with a medium of 1200-1500 mg/L COD strength, successful acclimated anaerobic growth of Bacillus spp. As hydrolysis proceeded, it was shown a long-term hydrolysis of granular kitchen organic fertilizer (Forma plastic Ltd.) was also important SHH origin - from HPLC profile. As examined, amendment of sugarcane black liquors, facilitated to have soluble pool, but donate low contribution of SHH. Provided limited carbon source for growth and acclimate EM [36]. In attempting to collect suitable liquid fertilizer through lengthening & acclimation duration, PSB consortia formed naturally and treated as stabilizing for the fertilizer through properly sunlight in the agriculture house. The co-fermentation culture of these EM consortia could proliferate and balanced growth after initiated inoculation.
Most commercial products of liquid fertilizer, as PS was designate for flowering & fruiting purpose [37], while EM Bacillus was better for antagonistic of pest and disease in growth stage [38]. In this experiment, we found EM Bacillus with PSC provide bioavailable phosphate beside nitrogen nutrient. Either organic fertilizer or SHH, provide less fertility as examined (Figures 6A & 6B). These results coincide SHH have grafted polar oxygen or hydroxyl groups related to effect on soil conditioning property. The nano sized molecular facilitated in penetrating through interacted bio-logical or mineral agent and responded in growth effect. Variant fertility responded & related to the nature of organic matter, or hydrolyzed product beside EM metabolite, with part of antagonistic microbe with metabolite active agent too. SHH hydrolysate might be the major effect that trigger the equilibrium state beside soil condition by proliferating in growth if it could be integrated in irrigation. The effect for faster nutrient delivery through irrigation contact is prospective, As seen liquid fertigation in this experiment have excellent proliferation for growth and enhance fruiting. These results demonstrated that humic SHH could combine EM for a balanced growth with high fertility for most plant if remediation required (Figures 7A & 7B).
Field observation of lattice breeding of sunflowers successfully discriminate effect over times of experimental compared. Organic fertilizer showed slow release and improved on supplement of SHH, which means its proliferation might directly from profound soil conditioning and some nutrient providing effect. In addition, boosted effect exerted when combine irrigated with Bacillus-PSC, which believed that active component produced in proliferate growth, their compatible with plant and rhizome community direct eventually reach a PGPR state and direct success cultivation. In conclude, the boost value of liquid fertigation of SHH with EM proved most reliable not only over 50 % more height and fruit obtained of sunflower growth (Figure 8), it generates a planting technology both in waste recovery and reuse for sustainable development, also possible for environmental engineering use in bio remediation implementation.
It would need in the near future for developing more environmentally compatible and higher productivity process with lowering salt content for field demonstration as well as integration to precision fertilization use.
CONCLUSION
The significant difference of sunflower plantation results between organic amendments as indicated that the nano-molecular – SHH revealed to be the crucial effector on linkages soil conditioning, fertilization with low disease severity. Thus, result splendid expression of even distribution and healthy growth. The building of harvest procedure had shown” SHH, through a nano-molecular pool (< 30 kda, 60 % soluble form after screen through 12 mesh) in acid hydrolyte – melanoid, was separable by molecular sieve cutting column. Beside harvest effectiveness of “SHH, as a nano-molecular pool of melanoid was demonstrated. Also, the sub screening strategy could be motivated by consulting the spectra metrical by its typical smooth broad spectrum (350-490 nm) and further presumed as multifunctional, hydrophilic in nature in surface. Thus, chemical adsorption process could further proceed higher purity expected. While these results indicate its unique property that drastically different from molasses with complex mixture property. These findings would be important for further preparative scale-up process. The incorporation with EM for testing their compatibility with macromolecular (from organic fertilizer, Product of Formosa Environmental Technology) hydrolyte was positive with acceptable distribution and elicited the plantation to stable fruiting. In conclude, the environmental friendly character of preparation including energy saving and practical fractionation, these green strategy having potential to develop a new way for biomaterials process contribute to matrix conditioner and precision agro-product.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This project was financially supported by the industry-academia cooperation / collaboration project, MingChi University of Technology, Taiwan, R.O.C. Constant consultancy from collaboration private company and Instrumental operation support by Environmental Resources Academia Yuan, MCUT.
REFERENCES
No Files Found
Share Your Publication :